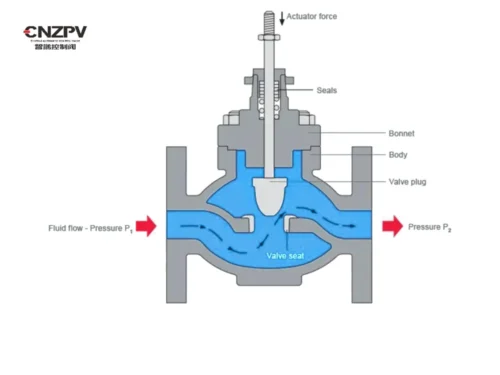
Fluoroplastics are widely used in valves due to their excellent chemical resistance, high – temperature resistance, and other properties. The following are common types of fluoroplastics used in valves and their differences:
1. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Chemical Structure and Properties
PTFE is a fully fluorinated polymer with a repeating unit of -CF2 – CF2 -. It has an extremely high degree of chemical inertness. It can withstand a wide range of corrosive chemicals such as strong acids (hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid), strong bases (sodium hydroxide), and organic solvents (such as benzene and toluene).
It has a very low coefficient of friction, which is close to that of ice on ice. This self – lubricating property makes it excellent for applications where smooth movement of valve components is required, such as valve stems and seats.
PTFE can operate over a wide temperature range, from – 200°C to +260°C.
Applications in Valves
It is commonly used to coat valve seats and seals. The coating provides a reliable seal that prevents leakage of fluids. In ball valves, for example, a PTFE – coated ball and seat can ensure tight shut – off even in harsh chemical environments.
PTFE – lined valves are also popular. The lining protects the valve body from corrosive media and provides a non – stick surface that reduces fouling and clogging.
Limitations
PTFE has relatively poor mechanical strength. It can be easily deformed under high pressure, so it may need additional reinforcement in high – pressure valve applications.
2. Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA)
Chemical Structure and Properties
PFA is a copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene and perfluoroalkyl vinyl ether. It has similar chemical resistance to PTFE. It can resist almost all chemicals and solvents, maintaining its integrity and performance in corrosive environments.
PFA has better mechanical properties than PTFE. It has higher tensile strength and flexural modulus, which means it can withstand greater mechanical stresses without deforming or breaking.
It also has a wide operating temperature range, typically from – 260°C to +260°C.
Applications in Valves
PFA is often used in high – performance valves where both chemical resistance and mechanical strength are required. For example, in valves used in semiconductor manufacturing processes, where precision and resistance to aggressive chemicals like hydrofluoric acid are essential.
It can be used to make valve diaphragms, seals, and linings. The diaphragms made of PFA can provide accurate control of fluid flow due to their good flexibility and strength.
Differences from PTFE
Compared to PTFE, PFA is more process – friendly in some manufacturing operations. It can be melt – processed more easily, allowing for more complex valve component shapes and designs.
3. Fluorinated Ethylene – Propylene (FEP)
Chemical Structure and Properties
FEP is a copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene and hexafluoropropylene. It has excellent chemical resistance, similar to PTFE and PFA. It can resist acids, bases, and many organic solvents.
FEP has a lower melting point than PTFE, which makes it easier to process. It can be extruded or injection – molded into various shapes.
It has good electrical insulation properties and is transparent, which can be advantageous in some valve applications where visual inspection of the interior is necessary.
Applications in Valves
FEP is often used to make transparent sight glasses or windows in valves. This allows operators to observe the flow of fluids inside the valve without opening it.
It can also be used to coat valve components to provide a protective and non – reactive surface. For example, coating the inner surface of a valve body to prevent chemical corrosion.
Differences from PTFE and PFA
FEP has a somewhat lower maximum continuous use temperature compared to PTFE and PFA, usually up to around 200°C. Its mechanical strength is also intermediate between PTFE and PFA.
CNZPV is highly professional in the field of fluorine-lined control valves. It has in-depth knowledge of these different fluoroplastics, understanding their respective chemical structures, properties, advantages and limitations. This enables us to precisely select the most suitable fluoroplastic materials for different valve applications based on specific requirements such as chemical resistance, mechanical strength and operating temperature range, thus ensuring the high quality and excellent performance of the fluorine-lined control valves it produces.